What to Look for in an Air Compressor Service Provider
Leave a CommentModern industrial production relies on compressed air to power equipment and keep operations running smoothly and reliably. In markets ranging from electronics and automotive to chemical and pharmaceutical, air compressors play a vital role.
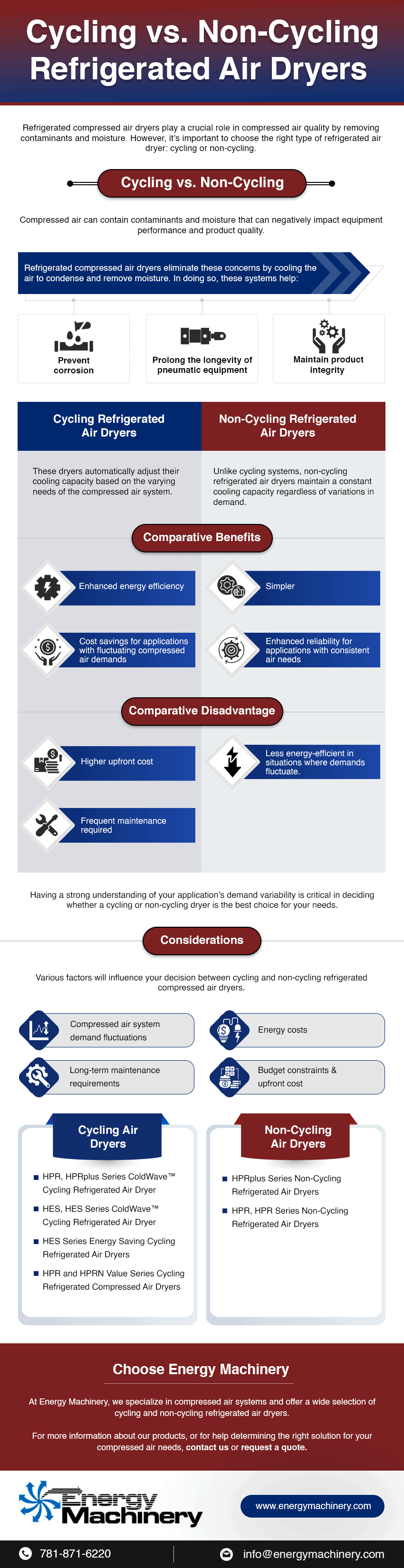
Choosing the right air compressor service provider can ensure you have continuous performance, minimal unscheduled downtime, and compressed air at the right volumes and pressures for your facility’s demands. Selecting the wrong provider, however, can result in inefficient processes, frequent disruptions, or even safety hazards due to poor equipment, training, and maintenance.
Key Factors in Selecting an Air Compressor Service Provider
Whether you’re selecting an air compressor service provider for the first time or changing providers, there are many criteria you can use to determine which company best meets your expectations and requirements.
Expertise and Experience
When providers have been in the industry for decades, it’s a key indicator that they consistently deliver effective, quality service. They’ll be familiar with a broad range of air compressor models and brands, making it likely that they’ve worked with equipment such as yours before. Such providers will have a deeper understanding of the equipment itself, making it possible for their team to suggest the right compressor or parts for your needs, ways to optimize your systems, what to look for when your compressor is experiencing a problem, and more. Finding a provider with multi-industry experience is also helpful, as it increases the chance that they’ve worked on jobs like yours.
Service and Product Offerings
Among the most important factors in selecting an air compressor service provider is that they offer a comprehensive range of services and products that meet all your unique needs to simplify operations. Examples of optimal offerings include:
- System audits and analyses
- Personalized preventive maintenance programs
- Emergency services to quickly troubleshoot equipment issues and reduce downtime
- Optimization expertise for upgrading equipment, improving energy efficiency, etc.
- Inventory of standard and aftermarket air compressor parts for optimal availability
Qualifications and Training
You might inquire about the training and certifications of a service provider’s technicians. A company that believes in continual improvement and invests in ongoing training is preferable to ensure that the provider is up to date on newer equipment, processes, and all applicable industry regulations and safety protocols. It’s an indicator that their team will have sufficient background knowledge to effectively meet your needs.
Responsiveness and Communication
Communication will make or break a business relationship. A company that’s difficult to reach or provides unclear communications isn’t an ideal choice. Look for a service provider that prioritizes customer satisfaction and responds promptly to all calls and inquiries. Particularly for emergencies, it’s also helpful if they have a dedicated sales representative available.
Cost and Transparency
Obtaining cost-effective services is a priority for most businesses. Look for service providers that offer rates that are competitive in the marketplace, along with clear and transparent pricing information. If a company’s pricing looks too good to be true, review for hidden fees and surcharges. A good service provider will be more than willing to go over their pricing details with you, offering additional information on how their services add value for customers.
Additional Air Compressor Service Provider Considerations
As you’re researching different options, review multiple sources of information, including the service provider’s website, any available testimonials, and reviews and ratings from clients. These resources can tell you more about the provider’s services as well as their reputation and local standing.
Additional factors you may want to consider include:
- Facility location(s) and service area
- U.S. based manufacturing
- Insurance and liability coverage
Choose Energy Machinery as Your Air Compressor Service Provider
Air compressors play a key role in facility operations, so choosing the right service provider is an important decision. Carefully assessing from multiple angles — quality and types of services, experience, price, and more — will help you find the right fit.
For industrial air compressor systems in Boston and the greater New England area, Energy Machinery, Inc. is here to help. The Energy Machinery team has been providing clients in diverse industries with industrial air compressors, as well as the parts and services to support them, since 1971. For over half a century, we’ve offered high-quality air compressors, installation and preventative maintenance services, factory-authorized warranty repairs, leak detection and energy audits, equipment rentals, and much more.
As a full-line air compressor distributor, we service and provide parts for most major makes and models, partnering with over 20 manufacturers. We maintain a large parts inventory of new, used, and hard-to-find components to best meet your needs and budget with fast turnarounds. Customer service is the cornerstone of our business, and our factory-certified technicians are available for 24-hour field service to handle any unexpected issues.
Contact us to learn more about the Energy Machinery difference, or request information for fast, comprehensive support.